What the “new” normal could look like…
|
Your action plan for uncertainty (2-minute watch)
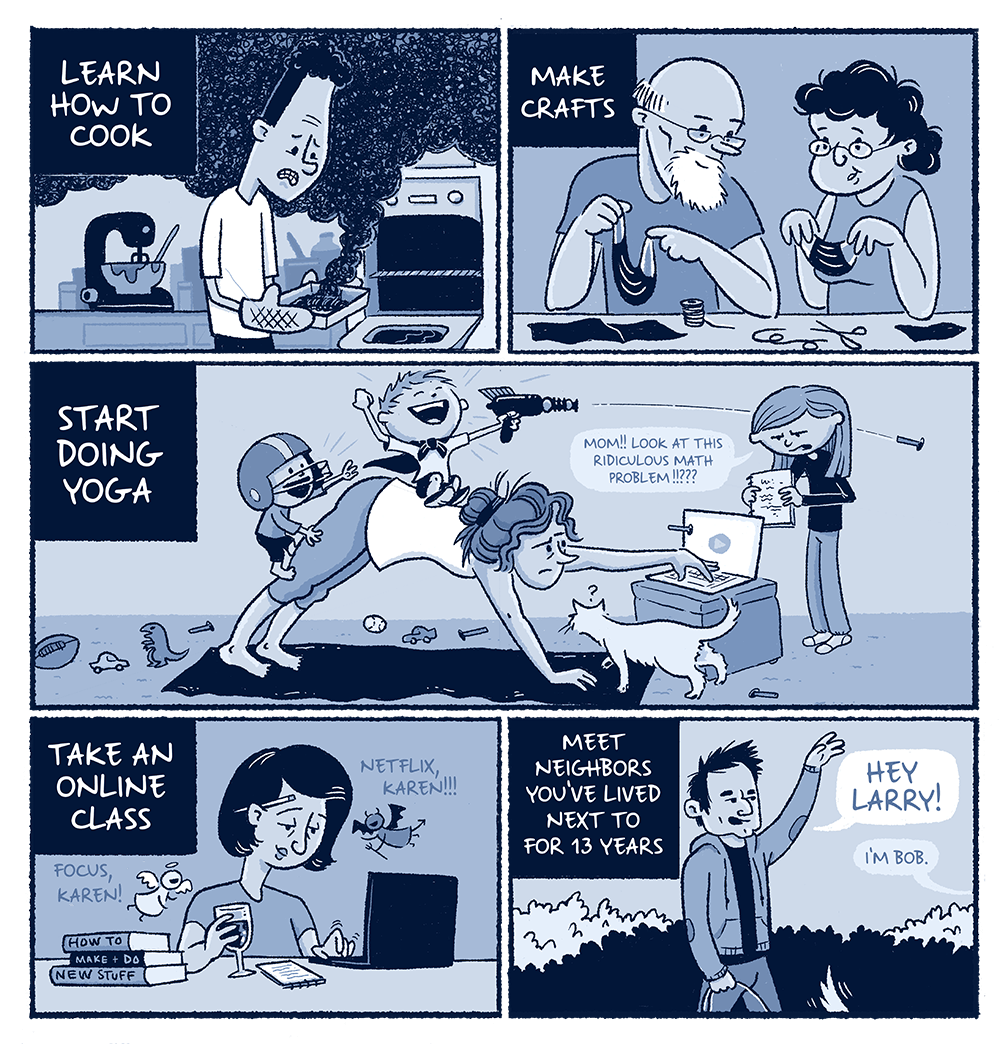
What lessons will you take from this?
So much is unknown.
Do we reopen or wait?
Are we past the peak? Or just over the first summit of a mountain range?
Are we safe yet?
After weeks of restrictions, it’s easy to feel that we’re swirling in a maelstrom of uncertainty, helpless to make decisions when so much remains unknown and out of our control.
The uncertainty, the personal losses many have experienced, and the everyday challenges of socially distant life can shake our foundation and cause us to lose touch with what’s most important.
I think that’s normal. We’ve traded a trip on the highway for an off-roading adventure. And we don’t know where it’s going to take us this year.
So let’s lean into the uncertainty. Let’s embrace it and use it as a wake-up call to explore and appreciate what really matters.
Our health. Our family, friends, and loved ones. Our home. Our community. Our compassion and creativity. Our resilience as human beings.
As for me, I have some moments of frustration, but I’m staying grounded by playing outside with our kids and working in the yard.
I’m also learning a lot about myself. I’ve learned that I really enjoy sitting face-to-face in the same room with clients, friends, and colleagues. I’ve learned that I’m not “camera ready” for Zoom meetings nor remote TV interviews, but I’m humbly trying to get better.
I’m working on gratitude and enjoying simple things like dinner-time conversations, our weekly visit with my parents, and fresh air.
I’m grateful to have a wonderful family, a comfortable home (aka The Bunker) and deeply meaningful work.
I’m grateful to have you.
On the professional side, I’m focused on what we can control on our clients’ behalf and staying abreast of what might come next. Our mantra right now is: “one day at a time.”
How are you? I’d love to hear how you are coping. What lessons are you learning about yourself? What have you had the courage to try for the first time? Hit “reply” and let me know.
This pandemic is scary. But it’s also a once-in-a-lifetime chance to hit the “reset” button and connect with the creativity, joy, and good old human ingenuity that can flourish within the limitations of pandemic life.
Eventually, we’ll recover from the pandemic. It’s not clear yet what that will look like, and we’ll likely see more hard days before we get there. Businesses will reopen, people will go back to work, the recession will pass, and the country will rebuild.
We will heal. But some marks will remain as reminders of our experience.
The Great Depression taught people to clip coupons and “make do or go without.” 9/11 upended our travel rituals and awareness of terrorism.
Some lessons from the pandemic will stay with us long after the immediate crisis fades. Some will be unconscious; maybe we’ll become a society of dutiful hand washers and social distancers.
Others will be lessons we consciously take with us about our values and ability to adapt to circumstances far beyond our control.
I’m hopeful and excited to see what we learn. Let’s make it good.
How has the pandemic changed your perspective? What new values and priorities will you bring out of your experiences? Email me at chrismullis@nstarcapital.com and let me know.
Be well,
Chris
 |
Chris Mullis, Ph.D. Founding Partner NorthStar Capital AdvisorsFinancial Planning. Wealth Management. Since 2006 AskNorthStar.com |
P.S. Do you know someone who is having a hard time and could use some financial advice? We’re holding a few spots open for folks who could use a professional’s help. If you can think of someone, please reply to this email or call (704) 350-5028 to let me know.
P.P.S. And don’t forget about our special COVID-19 pro bono planning we created to support individuals and families who can’t afford fiduciary advice and financial planning.
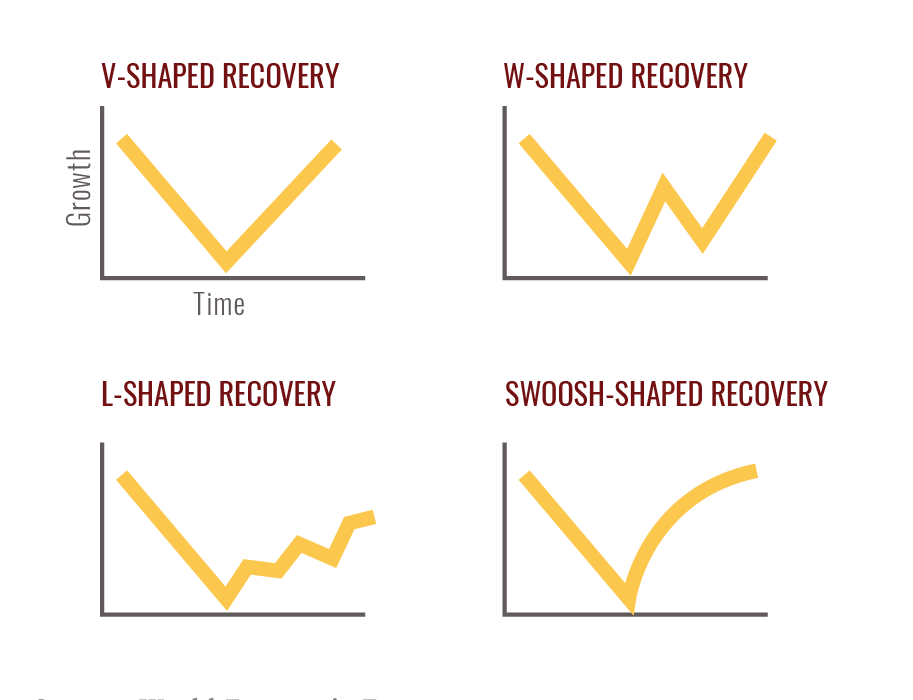
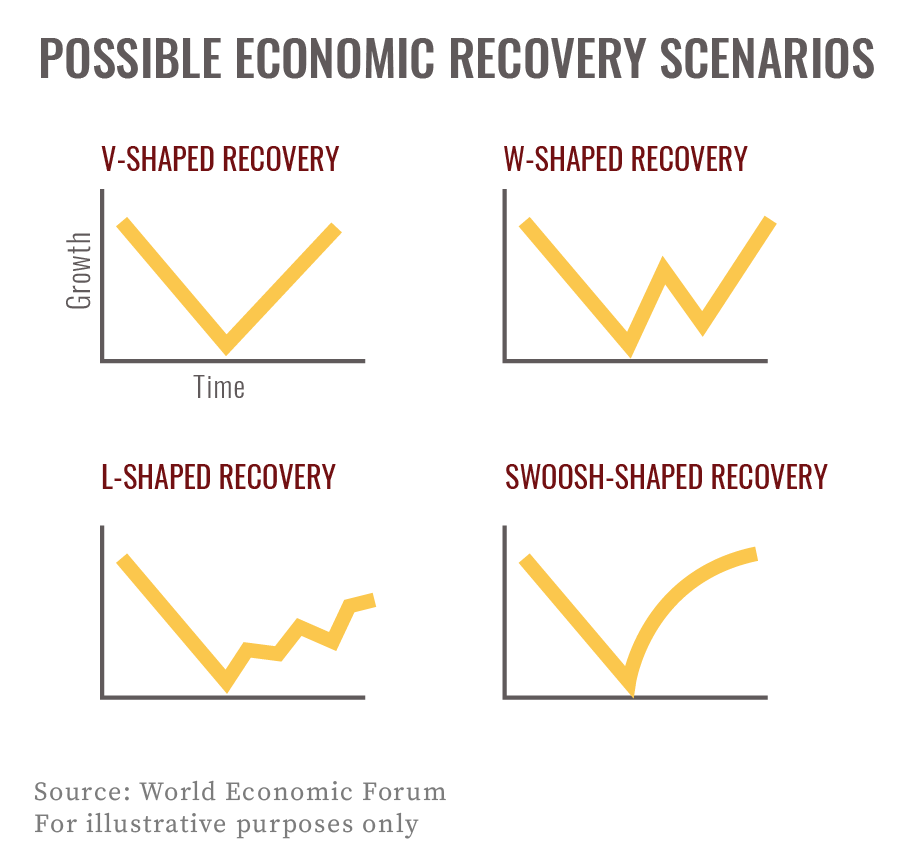
V, W, L, or Swoosh? (no, it’s not a meme)
|
Practical advice (and Frodo’s lesson)
|
This is why I’m an optimist
“The toilet paper had armed guards.”
“We celebrated my birthday with a dinner party over Zoom.”
“My officemate jumped on my desk and drooled on my keyboard during a meeting.”
One day, we’ll look back on these strange days and tell stories about the COVID-19 pandemic of 2020.
But right now, we’re getting through it. One day at a time.
How are you doing? What stories can you share with me about your life right now? Email me at chrismullis@nstarcapital.com and tell me. I’d love to hear about them.
In difficult times, it’s easy to think we are alone. Especially when our loved ones and support system are far away or reduced to virtual connections.
We are all learning how to adjust to a new world and stay grounded when headlines are blaring and our very health and well-being are under threat.
I’m working on being grateful for the great things in this life.
I’m grateful for my wife.
I’m grateful for our children.
I’m grateful for our family, friends, and neighbors.
I’m grateful for work that allows me to help people in my community get through times like these.
I’m grateful for you.
What are you grateful for?
Like WWII and 9/11, we’re living through days that will define future generations and change the very fabric of our society.
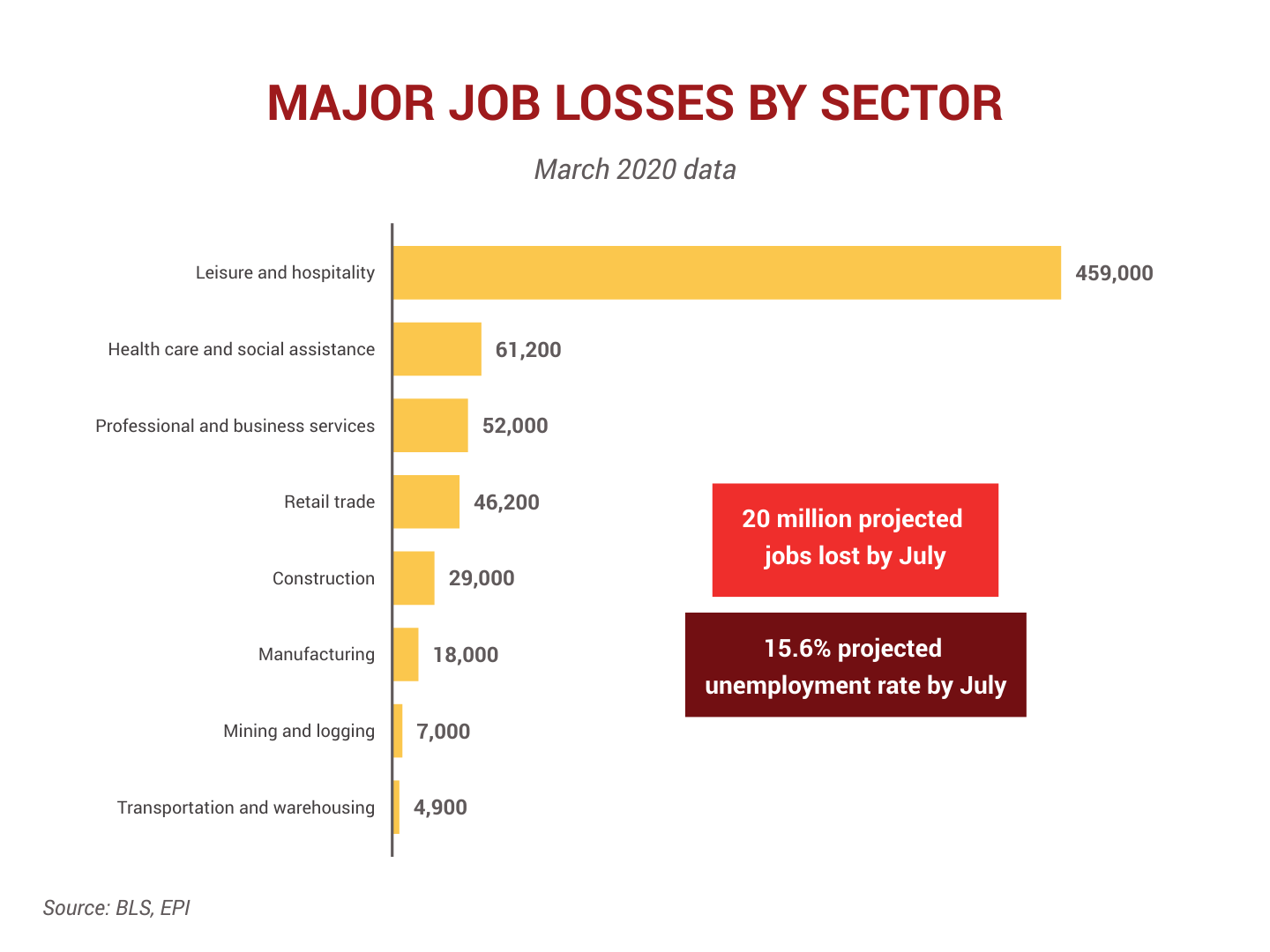
I don’t envy the policymakers making grim trade-offs between life, death, and the economy. How long do we socially distance? What about the 10 million+ who have lost jobs?1 Or the businesses that have been forced to close?
I hope with all my heart that each one of them has a financial plan and someone they can go to for advice. But my head knows better. I know that most Americans can’t survive a $1,000 emergency and only 17% have a financial adviser to help them.2
What trade-offs are we willing to make to protect those at greatest risk from the disease? We can’t put a dollar figure on human life. But we can put a dollar figure on the human cost of jobs lost and businesses closed.
The next few weeks are going to be tough for all of us. And I want you to know that I’m here for you.
Layoffs and furloughs are happening and I’m helping affected clients create a game plan to get through the next few months. If this happens to you or someone you love, please let me know immediately so I can help you determine if you’re eligible for special assistance. And, also please remember our COVID-19 pro bono program that we’ve launched to serve people who don’t normally have access to fiduciary advice.
How do we make good decisions with so much uncertainty and mixed information?
We make a choice:
We can choose to crumble under the weight of fear and uncertainty…
We can choose to simply hunker down and endure…
We can choose to grow, flourish, and come out stronger on the other side. We can be grateful for our blessings and focus on what’s within our control: our mindset, our behavior, and the actions we take.
I am fundamentally optimistic about humankind’s ability to weather this crisis and use it to grow.
I’m optimistic about how our society will adapt and change due to this crisis. Some of the greatest changes and innovations in history grew out of frightening, pessimistic times.
I’m optimistic about the heroes fighting the disease on the front lines.
I’m optimistic about the people helping friends, neighbors, and strangers stay safe and comfortable.
I’m optimistic that those with jobs will continue working to keep this country going while we wait and heal.
I’m optimistic about the innovators staying up late in labs, workshops, factories, and offices around the world to create vaccines, treatments, and tools to beat the virus.
I’m optimistic about the new inventions and technologies that will grow out of necessity.
I don’t know what challenges the world will throw at us in the coming days and weeks. I do know that I am grateful to be surrounded by smart, motivated people who push me to do better.
How can you show up for the people around you? How can you be your best self in these times?
How can I help you do it? Email or call and let me know.
Be safe and be well,
Chris
 |
Chris Mullis, Ph.D. Founding Partner NorthStar Capital AdvisorsFinancial Planning. Wealth Management. Since 2006 AskNorthStar.com |
2https://www.bankrate.com/banking/savings/financial-security-january-2019/
https://www.cnbc.com/2019/04/01/when-it-comes-to-their-financial-future-most-americans-are-winging-it.html
WCCB TV Interviews Dr. Chris Mullis
Source: WCCB TV / Local Financial Advisors Say “Stay the Course” Following Historic Market Drop
Dr. Chris Mullis, NorthStar’s Founding Partner, did an on-air interview with WCCB TV news anchor Drew Bollea discussing how people should think about their investments in the midst of a global panic induced by the coronavirus. (click image to watch video)
Ironically, this interview was recorded on March 9, 2020 — exactly 11 years to the day since the crescendo of global panic that marked the bottom of the 2007-09 bear market.
Here’s the memo that we sent clients and friends ahead of this interview that elaborates on the points made during the news report:
March 9, 2020
At this morning’s opening level of 2,764, the S&P 500 is down over 18% from its all-time high, recorded on February 19. Declines of that magnitude are fairly common occurrences — indeed the average annual drawdown from a peak to a trough since 1980 is close to 14%. But such a decline in barely a month is noteworthy, not for its depth but for its suddenness.
As we all know by now, the precipitants of this decline have been (a) the outbreak of a new strain of virus, the extent of which can’t be predicted, (b) the economic impact of that outbreak, which is equally unknown, and (c) most recently, the onset of a price war in oil. (That last one is surely a problem for everyone involved in the production of oil, but it’s a boon to those of us who consume it.)
The common thread here is unknowability: we simply don’t know where, when or how these phenomena will play out. And in my experience, the thing in this world that markets hate and fear the most is uncertainty. We have no control over the uncertainty; we can and should have perfect control over how we respond to it.
Or, ideally, how we don’t respond. Because the last thing in the world that long-term, goal-focused investors like us do when the whole world is selling is — you guessed it again — sell. Indeed, I welcome your inquiries around the issue of putting cash to work along in here.
On March 3, the erudite billionaire investor Howard Marks wrote, “It would be a lot to accept that the US business world — and the cash flows it will produce in the future — are worth 13% less today than they were on February 19.” How much more true this observation must be a week later, when they’re down 18%.
Be of good cheer. This too shall pass.
Mortgage Rates Hit All-Time Low (time to refi? let’s do the math)
 Growing your wealth is a combination of making money and saving money. Today we’re focused on the latter half of that equation. Current trends in the debt market could save thousands of dollars per year for mortgage borrowers.
Growing your wealth is a combination of making money and saving money. Today we’re focused on the latter half of that equation. Current trends in the debt market could save thousands of dollars per year for mortgage borrowers.
Mortgage rates fell to their lowest level on record today, pulled down by fears that the spread of the coronavirus could weigh on the U.S. economy.
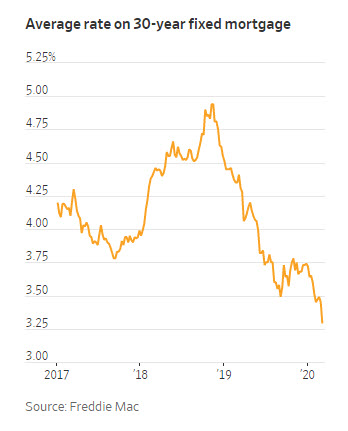
The average rate on a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage fell to 3.29% from 3.45% last week (see chart). This is its lowest level in its nearly 50-year history. The 15-year fixed-rate mortgage dropped to 2.79% from 2.95% the prior week.
Mortgage rates are closely linked to yields on the 10-year Treasury, which this week dropped below 1% for the first time following an emergency Federal Reserve rate cut on Tuesday. Expectations are that the 30-year fixed rate could even drop below 3% in the next few weeks.
These historically low interest rates represent a special opportunity to potentially save thousands of dollars per year by refinancing your mortgage.
Whether it makes sense to refinance depends on a host of factors.
We want to help you do the math and decide if you should refinance. We invite you to share the key parameters of your mortgage loan confidentially and securely using this link:
- Mortgage Loan Questionnaire
(if you own multiple properties, please submit one form per property)
We will dig into your data and make a detailed evaluation. We will come back and advise you on how much you could save now, or what’s your future trigger point for capturing significant savings as rates continue to evolve.
We’re strong believers in the abundance cycle. Please share this offer to family & friends and share the wealth!
The most valuable holiday gift for 2019?

(Holiday decorations & countdown courtesy of a very excited 11-year-old named Benjamin Mullis)
Let’s face it. Buying meaningful gifts for our family and friends is really, really hard. If you want to give something that has a larger impact long after the holiday season has passed, why not give the gift of financial education and wisdom for living a fulfilled life?
Given the academic background of our firm, I know the following is going to be a big shocker. Here at NorthStar, we love reading books and we love giving books as gifts! Below you’ll find the NorthStar Guide to Gifts That Pay Off. It’s full of our favorite book and money-related gift recommendations for those ages 4 to 94!
So what’s the most valuable holiday gift of 2019? A fun lesson in financial literacy and living your best life!
Happy shopping,
NorthStar Capital Adivsors
|
Recent Posts
-
Estimated Taxes, Marriage 2.0 and Cosmic Bumper Cars January 8,2026
-
Hidden Insurance Gaps That Threaten Your Wealth December 11,2025
Archives
- February 2026
- January 2026
- December 2025
- November 2025
- October 2025
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- December 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- November 2019
- October 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- May 2015
- April 2015
- March 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- July 2013
- June 2013
- May 2013
- April 2013
- March 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- November 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- July 2012
- June 2012
- May 2012
- April 2012
- March 2012
- February 2012
- January 2012
- December 2011
- November 2011
- October 2011
- September 2011
- August 2011
- July 2011
- June 2011
- May 2011
- April 2011
- March 2011
- February 2011
- January 2011
- November 2010
- October 2010
- September 2010
- August 2010
Categories
- 401(k)
- Annuities
- Behavior
- Best Practices
- Bonds
- Charitable Donations
- Economy
- Fees
- Fiduciary
- Financial Planning
- Investing 101
- Live Well
- Market Outlook
- Mutual Funds
- NorthStar
- Performance
- Personal Finance
- Planning
- Retirement
- Saving Money
- Scams & Schemes
- Seeking Prudent Advice
- Tax Planning
- Uncategorised
- Uncategorized
- Weekly Market Review